graphics
NOTE:
For technical reasons, all interactive-widgets plots in this documentation
are created using Holoviz’s Panel. Often, they will ran just fine with
ipywidgets too. However, if a specific example uses the param library,
or widgets from the panel module, then users will have to modify the
params dictionary in order to make it work with ipywidgets.
Refer to Interactive module for more information.
- spb.graphics.graphics.graphics(*args, aspect=None, axis_center=None, is_polar=None, legend=None, show=True, size=None, title=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, zlabel=None, xlim=None, ylim=None, zlim=None, fig=None, ax=None, update_event=None, **kwargs)[source]
Plots a collection of data series.
- Parameters:
- *args
Instances of
BaseSeriesor lists of instances ofBaseSeries.- axmatplotlib.axes.Axes
An existing Matplotlib’s Axes over which the symbolic expressions will be plotted.
- aspect(float, float) or str, optional
Set the aspect ratio of the plot. The value depends on the backend being used. Read that backend’s documentation to find out the possible values.
- axis_center(float, float), optional
Tuple of two floats denoting the coordinates of the center or {‘center’, ‘auto’}. Only available with
MatplotlibBackend.- backendPlot, optional
A subclass of
Plot, which will perform the rendering. Default toMatplotlibBackend.- fig
An existing figure. Be sure to also specify the proper
backend=.- is_polarboolean, optional
Default to False. If True, requests the backend to use a 2D polar chart, if implemented.
- legendbool, optional
Show/hide the legend. Default to None (the backend determines when it is appropriate to show it).
- showbool, optional
The default value is set to
True. Set show toFalseand the function will not display the plot. The returned instance of thePlotclass can then be used to save or display the plot by calling thesave()andshow()methods respectively.- size(float, float), optional
A tuple in the form (width, height) to specify the size of the overall figure. The default value is set to
None, meaning the size will be set by the backend.- titlestr, optional
Title of the plot.
- update_eventbool
If True, enable auto-update on panning. Default to False. Some backend may not implement this feature.
- use_latexboolean, optional
Turn on/off the rendering of latex labels. If the backend doesn’t support latex, it will render the string representations instead.
- xlabel, ylabel, zlabelstr, optional
Labels for the x-axis, y-axis or z-axis, respectively.
- xscale, yscale, zscale‘linear’ or ‘log’, optional
Sets the scaling of the x-axis, y-axis, z-axis, respectively. Default to
'linear'. Some backend might not implement this feature.- xlim, ylim, zlim(float, float), optional
Denotes the x-axis/y-axis/z-axis limits, respectively,
(min, max).- **kwargs
Refer to the documentation of a backend class in order to find more available keyword arguments.
- Returns:
- pPlot or InteractivePlot
If any of the data series is interactive (
paramshas been set) then an instance ofInteractivePlotis returned, otherwise an instance of thePlotclass is returned.
See also
plotgrid
Examples
Combining together multiple data series of the same type, enabling auto-update on pan:
>>> from sympy import * >>> from spb import * >>> x = symbols("x") >>> graphics( ... line(cos(x), label="a"), ... line(sin(x), (x, -pi, pi), label="b"), ... line(log(x), rendering_kw={"linestyle": "--"}), ... title="My title", ylabel="y", update_event=True ... ) Plot object containing: [0]: cartesian line: cos(x) for x over (-10.0, 10.0) [1]: cartesian line: sin(x) for x over (-3.141592653589793, 3.141592653589793) [2]: cartesian line: log(x) for x over (-10.0, 10.0)
(
Source code,png)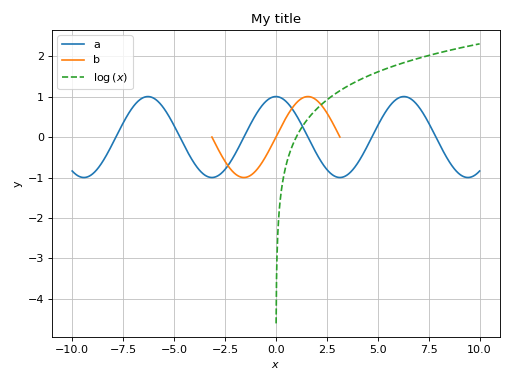
Combining together multiple data series of the different types:
>>> from sympy import * >>> from spb import * >>> x = symbols("x") >>> graphics( ... line((cos(x)+1)/2, (x, -pi, pi), label="a"), ... line(-(cos(x)+1)/2, (x, -pi, pi), label="b"), ... line_parametric_2d(cos(x), sin(x), (x, 0, 2*pi), label="c", use_cm=False), ... title="My title", ylabel="y", aspect="equal" ... ) Plot object containing: [0]: cartesian line: cos(x)/2 + 1/2 for x over (-3.141592653589793, 3.141592653589793) [1]: cartesian line: -cos(x)/2 - 1/2 for x over (-3.141592653589793, 3.141592653589793) [2]: parametric cartesian line: (cos(x), sin(x)) for x over (0.0, 6.283185307179586)
(
Source code,png)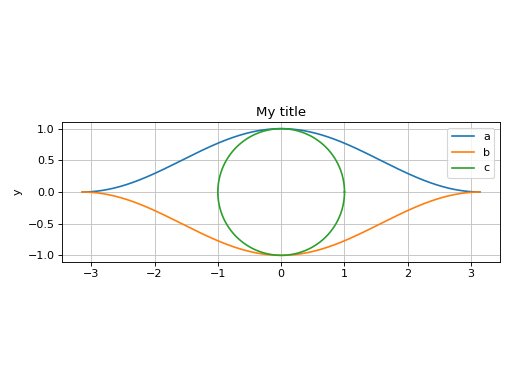
Plot over an existing figure. Note that:
If an existing Matplotlib’s figure is available, users can specify one of the following keyword arguments:
fig=to provide the existing figure. The module will then plot the symbolic expressions over the first Matplotlib’s axes.ax=to provide the Matplotlib’s axes over which symbolic expressions will be plotted. This is useful if users have a figure with multiple subplots.
If an existing Bokeh/Plotly/K3D’s figure is available, user should pass the following keyword arguments:
fig=for the existing figure andbackend=to specify which backend should be used.This module will override axis labels, title, and grid.
>>> from sympy import symbols, cos, pi >>> from spb import * >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> # plot some numerical data >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots() >>> xx = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 20) >>> yy = np.cos(xx) >>> noise = (np.random.random_sample(len(xx)) - 0.5) / 5 >>> yy = yy * (1+noise) >>> ax.scatter(xx, yy, marker="*", color="m") >>> # plot a symbolic expression >>> x = symbols("x") >>> graphics( ... line(cos(x), (x, -pi, pi), rendering_kw={"ls": "--", "lw": 0.8}), ... ax=ax, update_event=True) Plot object containing: [0]: cartesian line: cos(x) for x over (-3.141592653589793, 3.141592653589793)
(
Source code,png)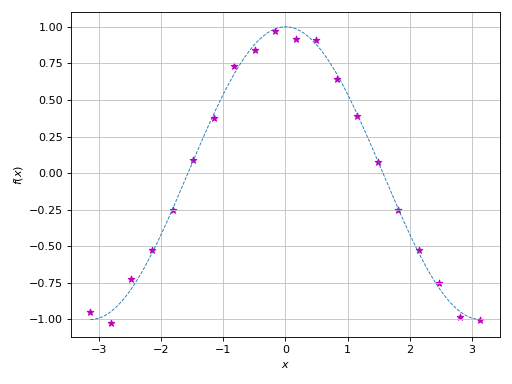
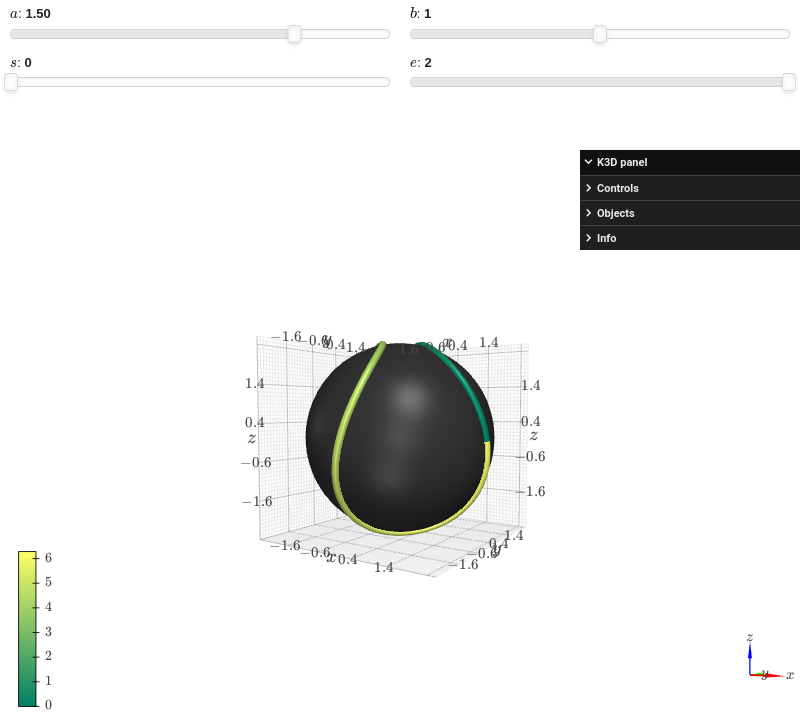
Interactive-widget plot combining together data series of different types:
from sympy import * from spb import * import k3d a, b, s, e, t = symbols("a, b, s, e, t") c = 2 * sqrt(a * b) r = a + b params = { a: (1.5, 0, 2), b: (1, 0, 2), s: (0, 0, 2), e: (2, 0, 2) } graphics( surface_revolution( (r * cos(t), r * sin(t)), (t, 0, pi), params=params, n=50, parallel_axis="x", show_curve=False, rendering_kw={"color":0x353535}, force_real_eval=True ), line_parametric_3d( a * cos(t) + b * cos(3 * t), a * sin(t) - b * sin(3 * t), c * sin(2 * t), prange(t, s*pi, e*pi), rendering_kw={"color_map": k3d.matplotlib_color_maps.Summer}, params=params ), backend=KB )